Never before has the need to diversify control of various operations and applications been more evident than now. In the fast-paced digital world, people are increasingly moving away from centralized applications opting for options that accord them some form of control. Consequently, decentralized applications are becoming increasingly popular.
What is a decentralized application (dApp)?
Simply put, it is an application that no single authority can claim to run or control. Additionally, the application cannot be shut off and is not susceptible to downtime as no single entity dictates its operations.
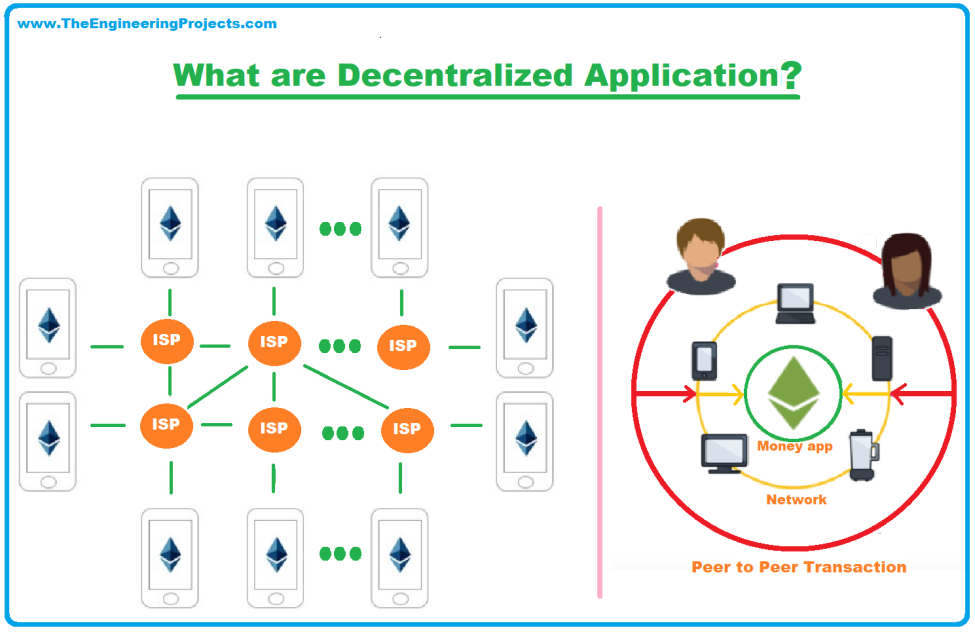
Contrary to perception, such applications don’t run on a blockchain alone. Likewise, there are peer-to-peer networks on top of which decentralized applications are embedded. The decentralized networks on top of which such applications run on are free from the control of any centralized entity such as the government, company, individual, or corporation.
Another important attribute of such applications is that no one single user can delete the content once the content is uploaded. It is common for administrators to pull down a message that they deem to contravene the app’s terms and conditions in normal applications, however with dApps, that is not possible.
How decentralized applications work
Decentralized applications can be web pages, desktop or mobile apps that operate independently without any control of a centralized entity. Their data is not hosted on any local or cloud servers but on a network of nodes that comes with an identical ledger.

Decentralized applications, back-end code, or smart contracts run on top of a decentralized network such as a blockchain instead of a centralized network. Consequently, they don’t rely on centralized locations for data storage; instead, they use smart contracts and developed blockchains such as Ethereum to store data and carry out operations.
A smart contract is simply an application that comes embedded with a set of rules that govern various operations, from mediating agreements to processing transactions. Once a dApp is deployed on a blockchain, it will operate based on the predetermined rules and carry out the operations it was primed to do in the first place.
DApps on a blockchain are controlled by the logic or rules written into the smart contract and not by an individual or a company.
DApps characteristics
Autonomy and the unanimous consensus is a key trait with all decentralized applications. What this means is that the source code that powers such applications is made public to the masses. Additionally, the consensus is achieved by all or the majority of the users agreeing. In this case, no one person makes decisions on behalf of the entire ecosystem.
All content in decentralized applications is stored in a decentralized blockchain where everybody can access with ease. In this case, there is no use of centralized storage facilities such as data centers. Decentralized application and cryptographic technology are commonly used for storage, thus protecting the network from the perils of centralized storage facilities.
Given that all the people in the network control all the aspects of the app, there is a need to have an incentive scheme for decentralized applications to be complete.
This means that there is a scheme whereby people are rewarded for their efforts in the development of the applications. In most cases, people are usually incentivized with cryptographic tokens.
Classifications of decentralized applications
Money dApps
These are decentralized applications that are designed to enhance the transfer of money worldwide by doing away with central authorities or intermediaries. Such applications speed up money transfer between two parties and across borders. Additionally, they are known to enhance security given the consensus mechanism deployed.
Business process management
Additionally, some dApps are being used to streamline processes and operations with minimum human intervention. Smart contracts are increasingly being used to automate the entire execution process when it comes to business operations.
For instance, smart contracts are finding their way into the supply chain operations whereby they can scan items and track shipments. In return, such applications can automatically initiate payments once certain conditions are met about the shipment.
Decentralized autonomous organization
Faceless organizations without leaders are increasingly cropping up. In this case, the organizations work and run based on predetermined rules and regulations programmed on top of a blockchain. Everything in the organization is operated on top of a blockchain, from voting to task allocation and the running of the day-to-day operations.
Given that everything is done on the blockchain, such organizations cannot stop once deployment starts.
DApps Benefits
Decentralized applications are addressing the data security menace that has clobbered centralized applications for years. The hosting of people’s information in local servers is proving to be inefficient given the persistent risk of being hacked. The cost of maintaining the servers is also proving to be high.
With dApps, people’s information is not stored on centralized servers, thus beyond the reach of hackers. Storing the data in a blockchain accords it the highest level of security as no one can pinpoint where exactly it is. Additionally, given that there is no organization operating a network, there is no motivation for the data to be sold.
In addition, the cost of maintaining a decentralized network is quite minimal as compared to the costs that centralized organizations pay for servers.
The open-source aspect of dApps means anyone can examine the source code that powers the decentralized applications. The provision gives an added level of transparency that centralized applications can offer.
The hurdles
For an application to be fully decentralized, there needs to be a sufficient number of nodes on the network. The higher the number of nodes, the more decentralized the app is and beyond the control of any centralized authority. However, that is not always the case, as many dApps have a small community or nodes, failing to meet the decentralization threshold.
The learning curve of dApps and how they operate is not that easy, especially for less computer-savvy users. The fact that users are required to hold specific tokens on a wallet to own private keys for token storage has significantly affected their popularity.
Bottom line
The need to move away from centralized applications and operations is increasingly fuelling demand for decentralized applications. These applications stand out partly because they move control from a central authority to the masses. Additionally, they stand out because of their enhanced security due to the use of blockchain technology.








